2020牛客寒假算法基础集训营3题解
A:牛牛的DRB迷宫I
 输入
输入
5 5
RBBBR
BBBBB
BBBDB
BDBBB
RBBBB25可以看到就是一个简单的dp题,然后再dp某一个点的时候,特判他能不能从左边和上边刷下来
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int mod=1000000007;
int dp[75][75],n,m;
char G[75][75];
int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%s",G[i]+1);
dp[1][1]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
if(i>1)dp[i][j]=(dp[i][j]+(G[i-1][j]=='R'?0:dp[i-1][j]))%mod;
if(j>1)dp[i][j]=(dp[i][j]+(G[i][j-1]=='D'?0:dp[i][j-1]))%mod;
}
}
cout<<dp[n][m];
return 0;
}B:牛牛的DRB迷宫II
 输入
输入
25输出
5 5
RBBBR
BBBBB
BBBDB
BDBBB
RBBBB说明
样例为《牛牛的DRB迷宫I》中的样例反过来。首先,不要被这个样例给虎了,这就是第一题的样例反过来,不是出题人标程序跑出来的结果, 我们考虑构造一个50x50的地图最多可能的结果,就是所有的位置全是B,那么构造的结果是\(C_{2n}^n \gg 10^9+7\),但是找不到规律qwq 于是构造一个二进制数,强制对角线为\(2^n\),如图 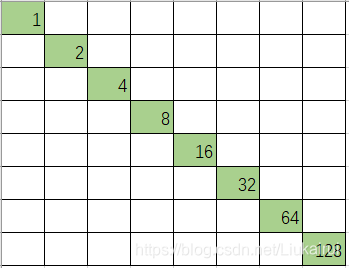 首先,证明他的可行性,这样最大可以构造数字为\(2^{50}>2^{32}>10^9+7\),说以这样构造是可行的 然后考虑如何构造这样的一个迷宫,由于数字只能从左上到右下流动,所以要想2倍,比较好的方法是
首先,证明他的可行性,这样最大可以构造数字为\(2^{50}>2^{32}>10^9+7\),说以这样构造是可行的 然后考虑如何构造这样的一个迷宫,由于数字只能从左上到右下流动,所以要想2倍,比较好的方法是 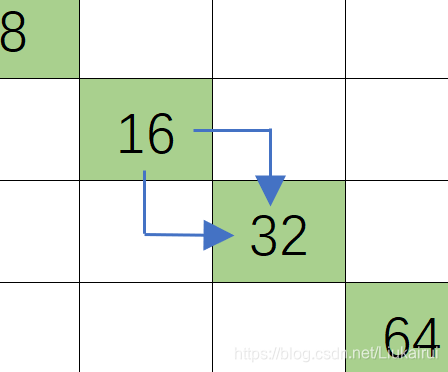 那么,我们的构造方法是
那么,我们的构造方法是 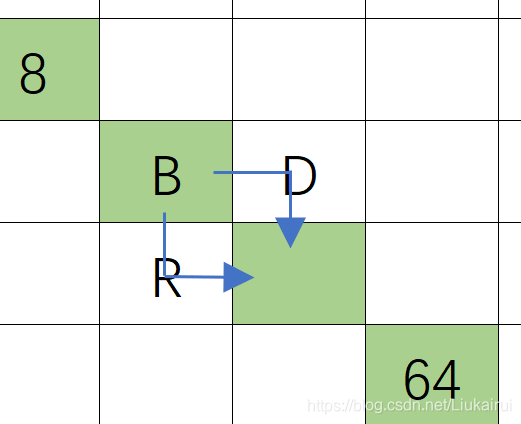 左上角的绿块一定要是
左上角的绿块一定要是B,右面那个可以是B也可以是D因为即使右边是B,向右流过去也不会影响下面的,但是有可能会影响64那个块,所以我们让右边一定是D,同理下面那个可以是R也可以是B,但是我们暂定为R,于是暂时构造迷宫如图 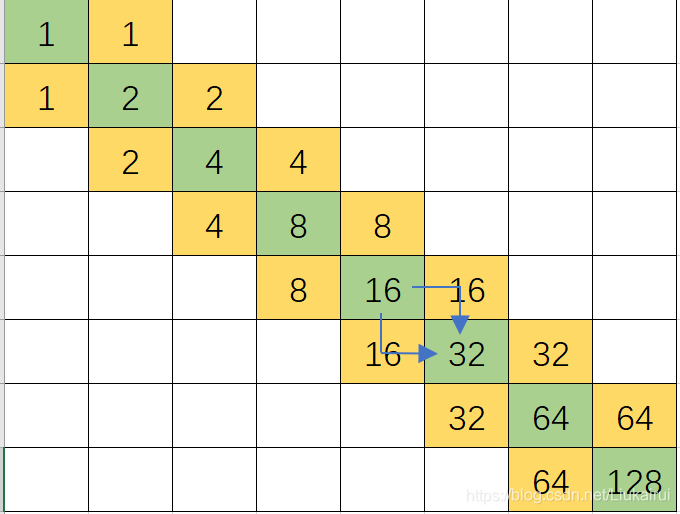
 错的思路: 这就好办了,我们把给的数分解为二进制,0就不选,1就选,例如25=11001(2进制) 蓝色是选,绿色是不选
错的思路: 这就好办了,我们把给的数分解为二进制,0就不选,1就选,例如25=11001(2进制) 蓝色是选,绿色是不选 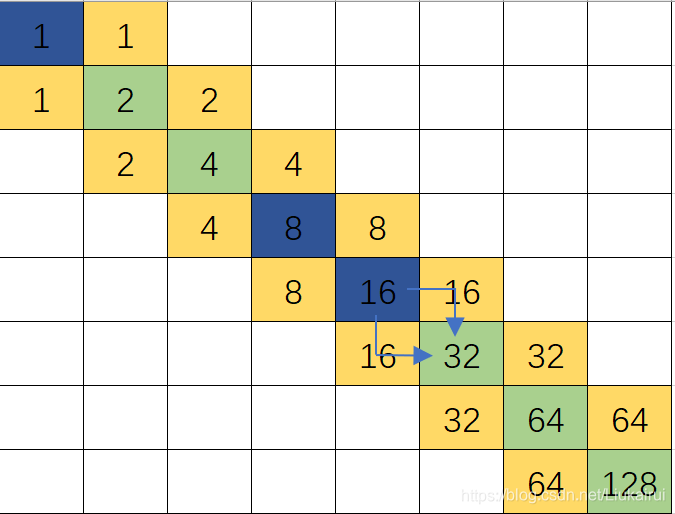 于是写出代码
于是写出代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main(){
long long k,len;
scanf("%lld",&k);
for(len=0;(1<<len)<=k;len++);
printf("%d %d\n",len,len);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
for(int j=0;j<len;j++){
if(j-i==1)printf("B");
else if(i-j==1){
if(k)printf("B");
else printf("D");
k>>=1;
}
else if(i==j)printf("B");
else if(i<j)printf("R");
else printf("D");
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}这是错的,因为我们的二进制不选,下一个就会受影响,如图 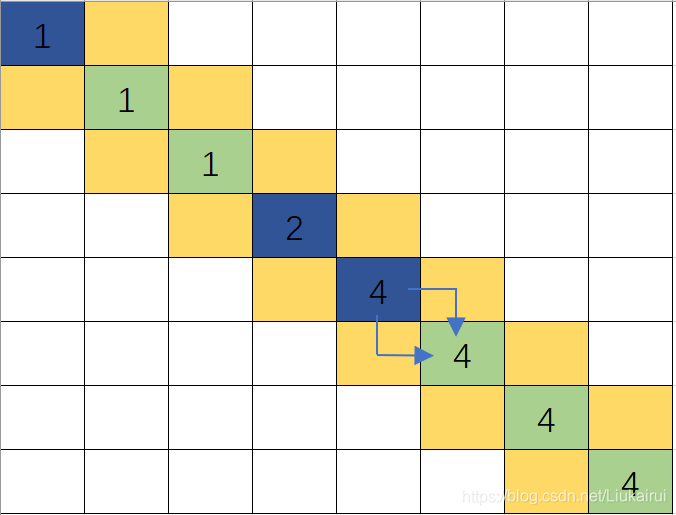 所以这个对角线上的数字必须保留! 那如何优雅的表示选或者不选呢?? 首先,右上方的数字这么填写呢?? 一旦填写往下走到对角线上就会对对角线造成干扰,如图
所以这个对角线上的数字必须保留! 那如何优雅的表示选或者不选呢?? 首先,右上方的数字这么填写呢?? 一旦填写往下走到对角线上就会对对角线造成干扰,如图 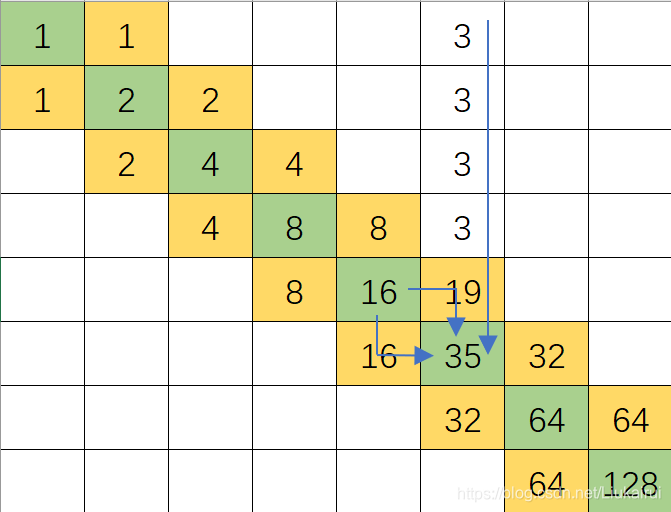 所以,不要让他对对角线造成干扰,我们把右上方黄线全部设为
所以,不要让他对对角线造成干扰,我们把右上方黄线全部设为D!!! 这样右上方白块全都是0了,右上全写R 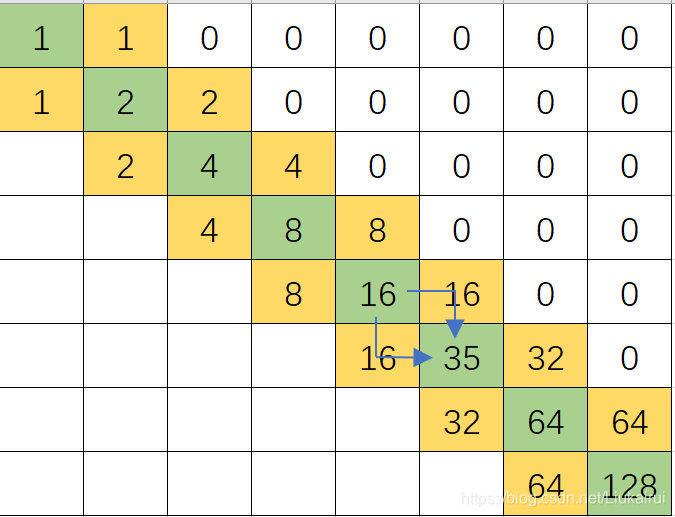
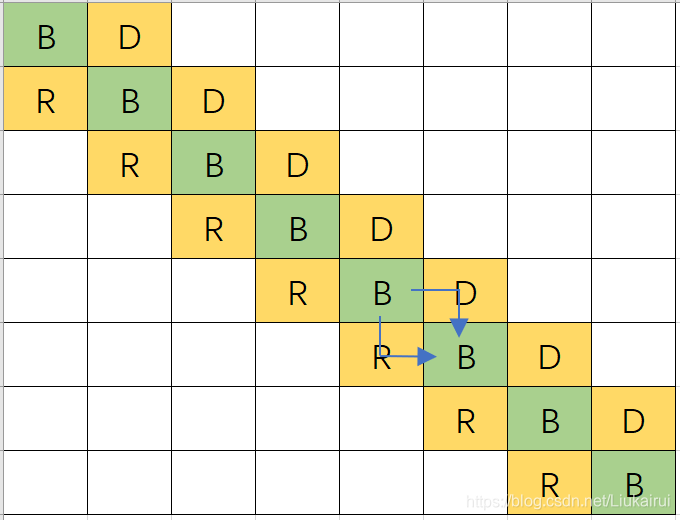
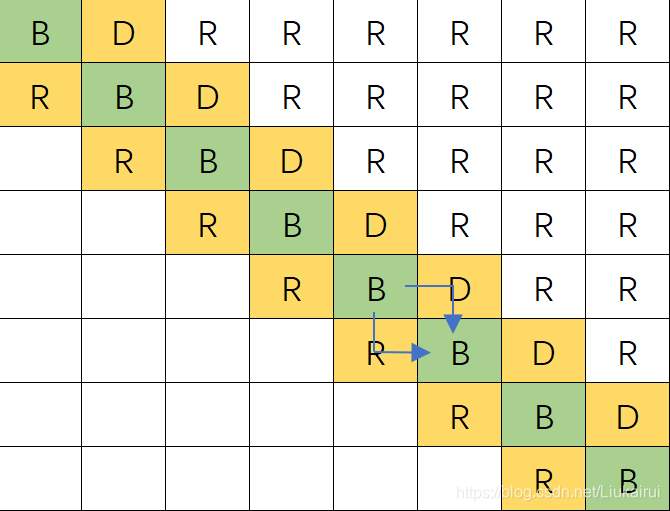 我们想让右下角数字承担选择转运的作用 首先一个要选的数字不能向右走,我们构造如下,首先把最后一个128要删去了,为啥,最后一个要放ans,我们假设
我们想让右下角数字承担选择转运的作用 首先一个要选的数字不能向右走,我们构造如下,首先把最后一个128要删去了,为啥,最后一个要放ans,我们假设77是最后要的结果 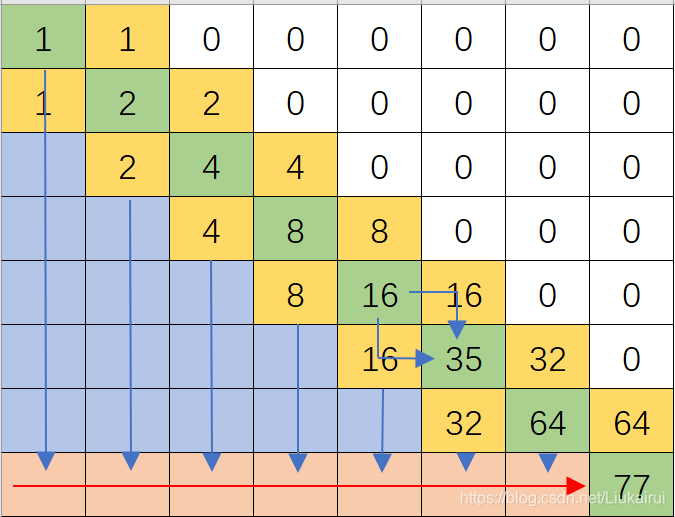 让蓝色承担往下走的功能,红色是往右走
让蓝色承担往下走的功能,红色是往右走 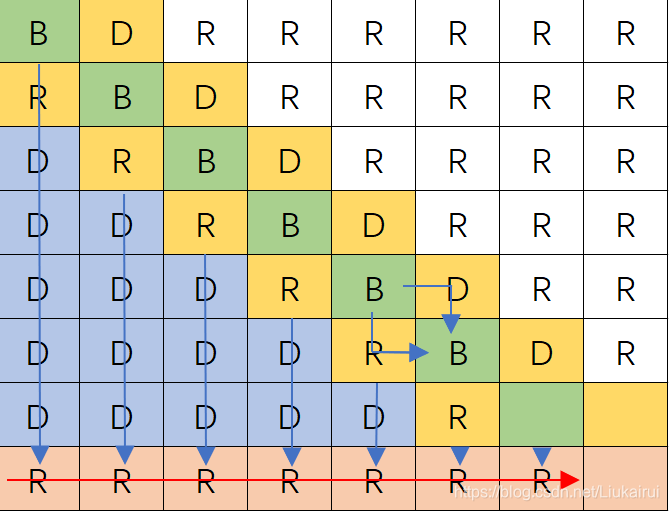 那如何让数据往下流呢?
那如何让数据往下流呢? 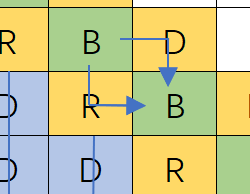 比如现在他就流不下来 这么处理呢? 把他改成红色
比如现在他就流不下来 这么处理呢? 把他改成红色 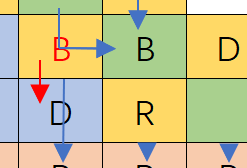 这就流下卡了 那么我们就让想让他流下来的写成B,不想流下来的写成R,就这样就做到了
这就流下卡了 那么我们就让想让他流下来的写成B,不想流下来的写成R,就这样就做到了 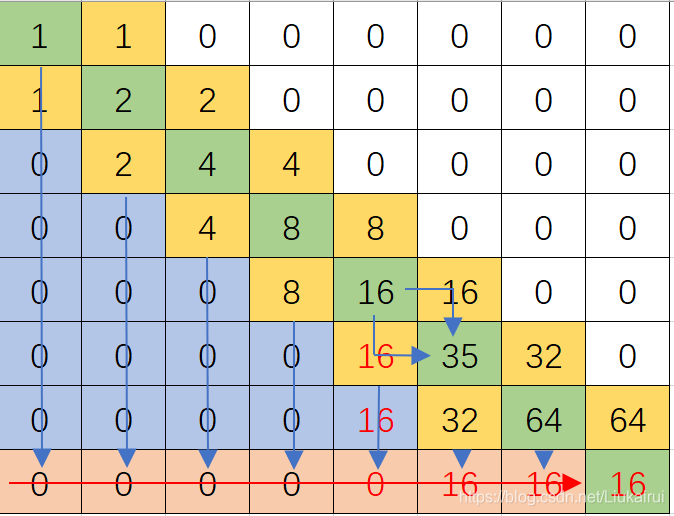 所以,我们就做到了这一点,例如我们要处理一个
所以,我们就做到了这一点,例如我们要处理一个77这样写 77= 1001101(二进制) 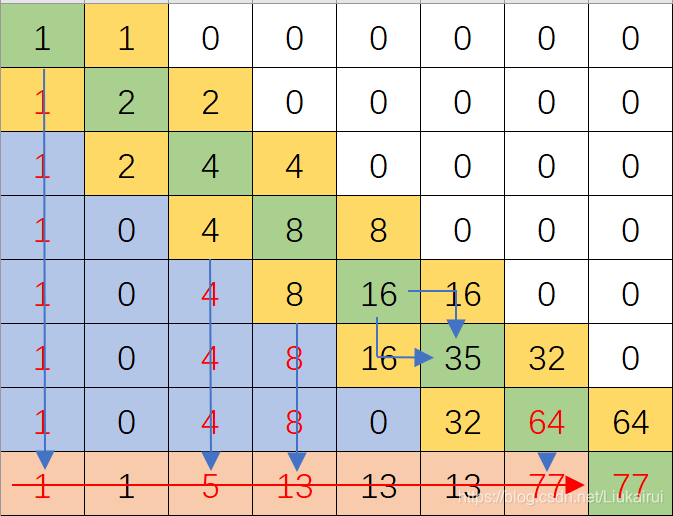
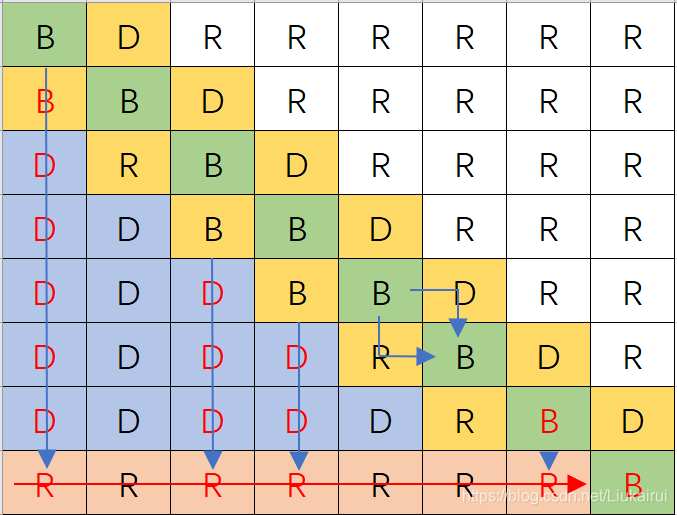 错误思路!!!: 轻松写出代码
错误思路!!!: 轻松写出代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main(){
long long k,len=0;
scanf("%lld",&k);
for(len=0;(1<<len)<=k;len++);
if((1<<len)==k)len++;len++;
printf("%lld %lld\n",len,len);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
for(int j=0;j<len;j++){
if(i==j)printf("B");
else if(j-i==1)printf("D");
else if(j-i>1)printf("R");
else if(i-j>1)printf((i==len-1?"R":"D"));
else{
if(k&1)printf("B");
else printf("R");
k>>=1;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}有问题!! 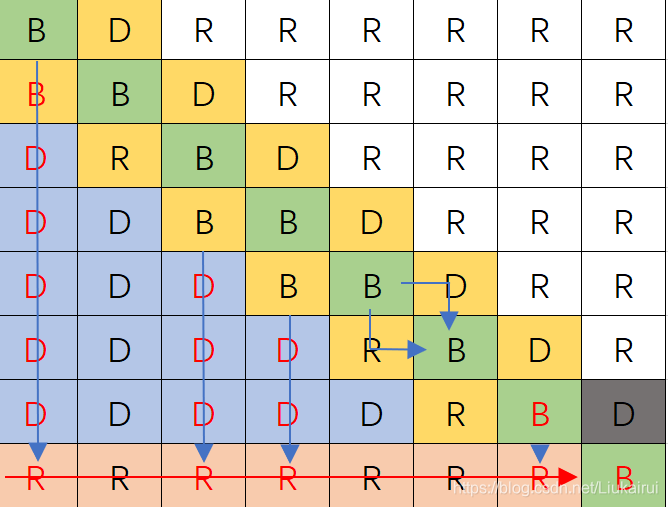 这个灰色的表格,他是构造的时候让他构造主对角线才写为
这个灰色的表格,他是构造的时候让他构造主对角线才写为D,但是我们不能让他往下走,现在最后一个表格不是\(2^n\)了,写为R 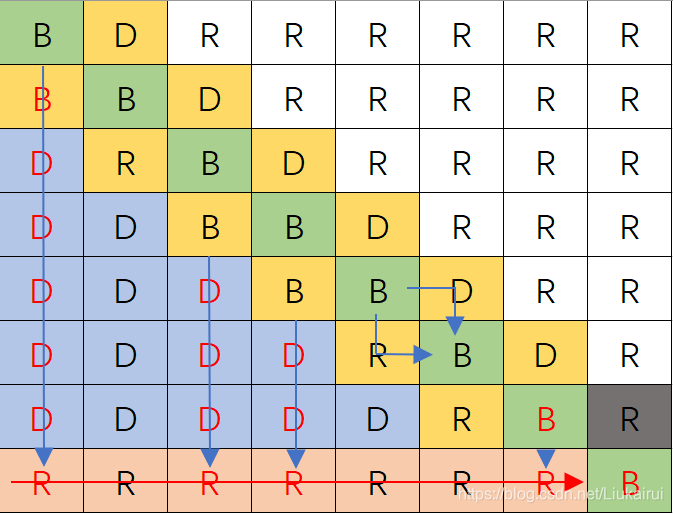 所以再加一个特判
所以再加一个特判
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main(){
long long k,len=0;
scanf("%lld",&k);
for(len=0;(1<<len)<=k;len++);
if((1<<len)==k)len++;len++;
printf("%lld %lld\n",len,len);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
for(int j=0;j<len;j++){
if(i==len-2&&j==len-1)printf("R");
else if(i==j)printf("B");
else if(j-i==1)printf("D");
else if(j-i>1)printf("R");
else if(i-j>1)printf((i==len-1?"R":"D"));
else{
if(k&1)printf("B");
else printf("R");
k>>=1;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}但只有case通过95% 有两个bug, 1. \(k>10^9+7\)要mod回来 2. k=0的时候的解,我试了三个方法,这个spj只支持最后一个
if(k==0){printf("0 0");return 0;}
if(k==0){printf("No solution");return 0;}
if(k==0){printf("2 2\nBR\nDB");return 0;}最后写出AC代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main(){
long long k,len=0;
scanf("%lld",&k);
k=k%1000000007;
// if(k==0){printf("0 0");return 0;}
if(k==0){printf("2 2\nBR\nDB");return 0;}
// if(k==0){printf("No solution");return 0;}
for(len=0;(1<<len)<=k;len++);
if((1<<len)==k)len++;len++;
printf("%lld %lld\n",len,len);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
for(int j=0;j<len;j++){
if(i==len-2&&j==len-1)printf("R");
else if(i==j)printf("B");
else if(j-i==1)printf("D");
else if(j-i>1)printf("R");
else if(i-j>1)printf((i==len-1?"R":"D"));
else{
if(k&1)printf("B");
else printf("R");
k>>=1;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}真的是奇怪的构造qwq
C:牛牛的数组越位
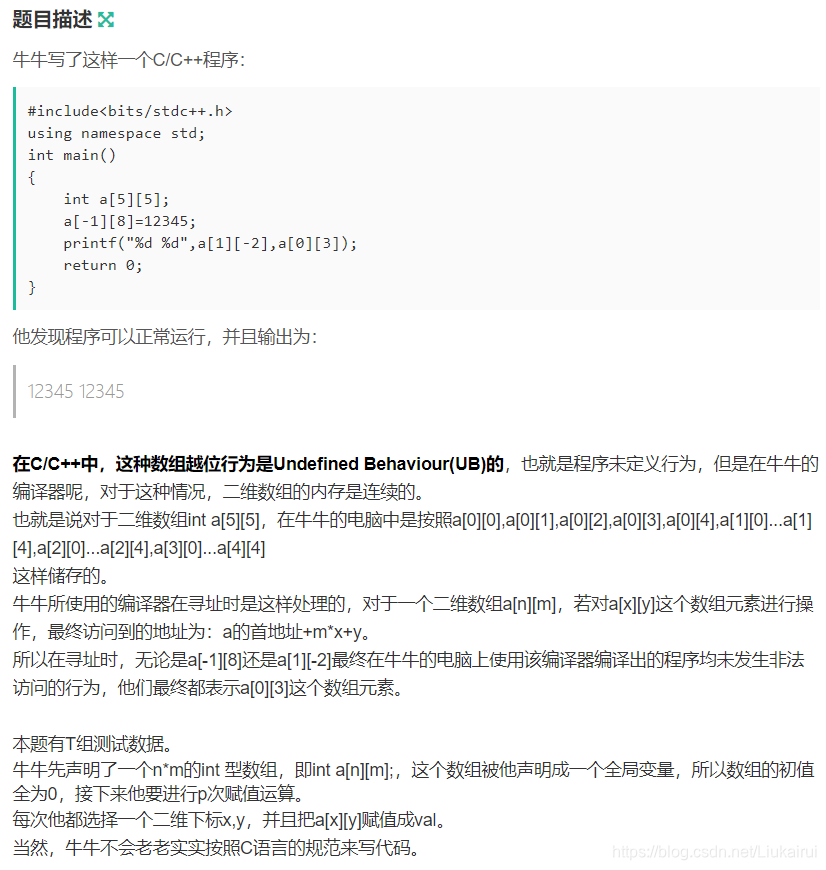 输入
输入
4
2 4 8
-1 4 1
1 -3 2
2 -6 3
0 3 4
-1 8 5
-2 13 6
-100 406 7
100 -393 8
5 5 1
-1 8 1234
10 10 1
5 -51 1
1 1 1
0 0 7输出
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
Undefined Behaviour
0 0 0 1234 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
Undefined Behaviour
Runtime error
7
Accepted备注:
无论是否发生数组越位或者非法访问,输入数据都要完整读入。
题目中的代码不符合C/C++规范,在不同编译器中由于实现不同运行的结果也可能不同,请勿依赖特定编译器对于UB的实现。:)签到题,二维数组用一维模拟即可,但是比较奇怪的是比赛写的一直是TLE AC代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
long long a[1103550];
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
int state=0;
long long n,m,p,x,y,v;
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&n,&m,&p);
for(int i=0;i<p;i++){
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&x,&y,&v);
if(state==2)continue;
long long pos=m*x+y;
if(pos<0||pos>m*n-1){
state=2;
}
else{
if(x<0||y<0||x>=n||y>=m)
state=1;
a[pos]=v;
}
}
if(state==2)cout<<"Runtime error"<<endl;
else{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)cout<<a[i*m+j]<<(j==m-1?"":" ");
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<(state==1?"Undefined Behaviour":"Accepted")<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}D:牛牛与二叉树的数组存储

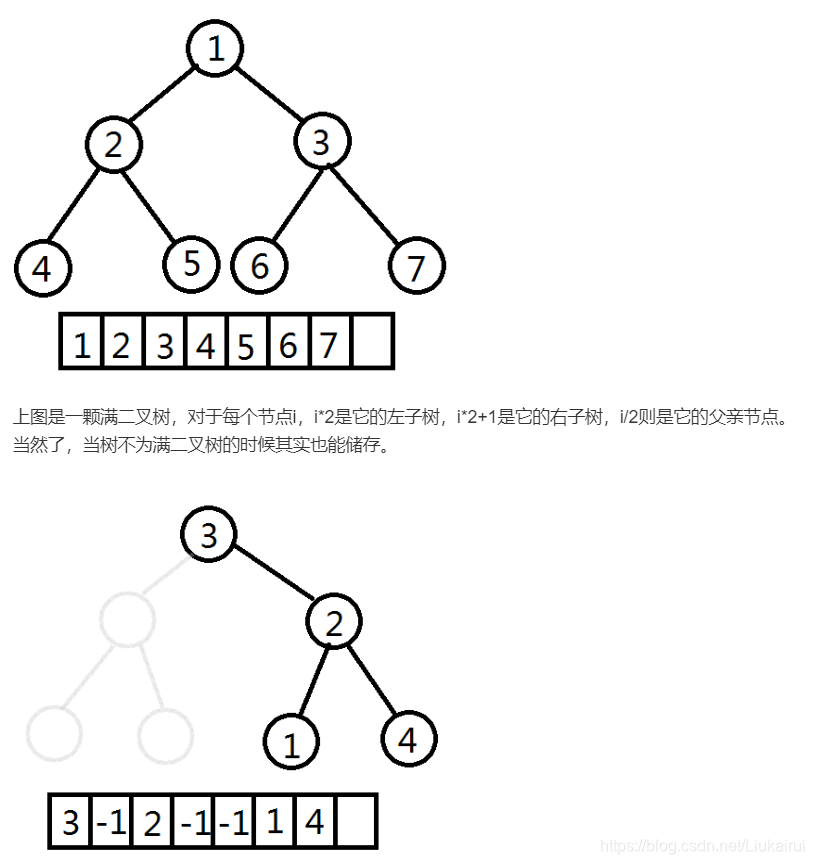
 输入
输入
7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7输出
The size of the tree is 7
Node 1 is the root node of the tree
The father of node 1 is -1, the left child is 2, and the right child is 3
The father of node 2 is 1, the left child is 4, and the right child is 5
The father of node 3 is 1, the left child is 6, and the right child is 7
The father of node 4 is 2, the left child is -1, and the right child is -1
The father of node 5 is 2, the left child is -1, and the right child is -1
The father of node 6 is 3, the left child is -1, and the right child is -1
The father of node 7 is 3, the left child is -1, and the right child is -1输入
7
3 -1 2 -1 -1 1 4输出
The size of the tree is 4
Node 3 is the root node of the tree
The father of node 1 is 2, the left child is -1, and the right child is -1
The father of node 2 is 3, the left child is 1, and the right child is 4
The father of node 3 is -1, the left child is -1, and the right child is 2
The father of node 4 is 2, the left child is -1, and the right child is -1前几天刚学了重口味线段树,即线段树的堆式存储 AC代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int ss[900050],n,cnt=0,pos[900050];
inline int read(){
int k=0;
char f=1;
char c=getchar();
while(c>'9'||c<'0')
if(c=='-'){
f=-1;
c=getchar();
}
while(c<='9'&&c>='0'){
k=k*10+c-'0';
c=getchar();
}
return k*f;
}
int main(){
n=read();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int t=read();
ss[i]=t;
if(t>0){cnt++;pos[t]=i;}
}
int root;
for(root=1;root<=n;root++)if(ss[root]!=-1)break;
cout<<"The size of the tree is "<<cnt<<endl;
cout<<"Node "<<ss[root]<<" is the root node of the tree"<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++){
root=pos[i];
cout<<"The father of node "<<ss[root]<<" is "<<(ss[root>>1]==0?-1:ss[root>>1])<<", the left child is "<<(ss[root<<1]==0?-1:ss[root<<1])<<", and the right child is "<<(ss[(root<<1)+1]==0?-1:ss[(root<<1)+1])<<endl;
}
return 0;
}E:牛牛的随机数
 输入
输入
2
3 5 7 8
1 3 3 5输出
500000011
222222228说明
a可取3,4,5,b可取7,8
3⊕7=4,4⊕7=3,5⊕7=2
3⊕8=11,4⊕8=12,5⊕8=13
共6种情况,答案为(4+3+2+11+12+13)/6=45/6=15/2=15*2^(-1)mod(10 ^9+7)=15*500000004%mod=500000011因为是区间计数问题,所以使用数位dp 作者:四糸智乃 链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/discuss/365306?type=101&order=0&pos=1&page=2 来源:牛客网
有两种思路,第一种是拆位后直接数位DP。 首先考虑二进制的个位产生的贡献,那么二进制个位产生的贡献有两部分: \([l_1,r_1]\)区间内个位为0的数字乘以#[l_2,r_2]\(区间内个位为1的数字。\)[l_1,r_1]\(区间内个位为1的数字乘以\)[l_2,r_2]\(区间内个位为0的数字。 做一个二进制位的数位DP,用于统计该数位0与1的个数。 假设\)x 中二进制的个位产生0的数目为¥cntx_0cnt二进制的个位产生1的数目为\(cntx_1\) \(y \in [l_2,R_2]\)中二进制的个位产生0的数目为\(cnty_0\)二进制的个位产生1的数目为\(cnty_1\) 那么就产生了\(cnty_0*cntx_1+cntx_0*cnty_1\)的贡献。 如果是二进制的十位呢,那么就是\((cnty_0*cntx_1+cntx_0*cnty_1)*2\)。 那么二进制的第k位的贡献就为\((cnty_0*cntx_1+cntx_0*cnty_1)*2^k\)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const long long mod=(int)1e9+7;
int i,i0,T;
long long cnta[70],cntb[70],dp[70][70][2],a[70];
long long dfs(int len,bool maxi,int k,bool f)
{
if(dp[len][k][f]!=-1&&maxi==0)return dp[len][k][f];
long long cnt=0;
if(!len)return f;
int maxn=maxi?a[len]:1;
for(int i=0;i<=maxn;i++)cnt+=dfs(len-1,maxi&&i==a[len],k,f||len==k&&i);
return maxi?cnt:dp[len][k][f]=cnt;
}
long long div(long long tmp,int k)
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
int p=0;
while(tmp)a[++p]=tmp%2,tmp/=2;
return dfs(p,1,k,0);
}
long long inv(long long x,long long mod)
{
long long k=mod-2,ans=1;
while(k)
{
if (k&1) ans=ans*x%mod;
x=x*x%mod;
k>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
long long l1,r1,l2,r2,p=1,ans=0;
scanf("%lld %lld %lld %lld",&l1,&r1,&l2,&r2);
l1--,l2--;
for(i=1;i<=60;i++,p*=2)
{
cnta[i]=div(r1,i)-div(l1,i);
cntb[i]=div(r2,i)-div(l2,i);
ans+=(cnta[i]%mod*((r2-l2-cntb[i])%mod)%mod+cntb[i]%mod*((r1-l1-cnta[i])%mod)%mod)*(p%mod)%mod;
ans%=mod;
}
ans%=mod,ans+=mod,ans%=mod;
ans=ans*inv(((r1-l1)%mod)*((r2-l2)%mod)%mod,mod)%mod;
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}F:牛牛的Link Power I
 输入
输入
3
101输出
2输入
5
00110输出
1输入
6
000010输出
0记录每个1点的位置 对于第i个点,我们只要计算他以前的点即可 定义\(pos_i\)是第i个节点的位置\(sum \_ pos_i\)是前i个位置的\(pos\)和,对于第i个位置 以前的节点和为 \[ \sum \limits_{j=1}^{i}\left \{ pos_i-pos_j \right \} = \sum \limits_{j=1}^{i}pos_i-sum \_ pos_{i-1}=i \times pos_i - sum \_ pos_{i-1} \] 写一个前缀和得到\(sum \_ pos_i\) 代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int mod=1000000007;
int cnt=0,n,pos[100050];
char ss[100050];
long long ans=0;
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%s",ss);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(ss[i]=='1')pos[cnt++]=i+1;
}
int k=-(cnt-1);
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++,k+=2)ans=(ans+(k*pos[i]))%mod;
cout<<ans;
}G:牛牛的Link Power II
 输入
输入
5
00001
7
1 1
2 5
2 1
1 2
1 4
1 3
1 1输出
0
4
0
0
0
2
4
10修改由于要频繁修改我们使用线段树来处理对于第i的点,我们需要一个获得
- i前面所有1的pos和
- i前面所有1的数目
- i后面所有1的pos和
- i后面所有1的数目
对于查询一个区间我们需要两个数据作为返回值pair<1的pos总和,1的数目>, 所以线段树写成pair<long long, long long>数组的形式 注意pair合并的写法
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#define LC (p<<1)
#define RC (LC|1)
#define M ((l+r)>>1)
#define mod 1000000007
#define MAX_N 100050
using namespace std;
typedef pair<long long,long long> PII; //pos cnt
int n,m;
long long sumn=0,cnt=0,ans=0;
PII ss[MAX_N<<2];
void up(int p){
ss[p].first=(ss[LC].first+ss[RC].first)%mod;
ss[p].second=(ss[LC].second+ss[RC].second)%mod;
}
void modify(int p,int x,int v,int l,int r){
if(l==r){
if(v==1)ss[p]=make_pair(l,1);
if(v==-1)ss[p]=make_pair(0,0);
return;
}
if(x<=M)modify(LC,x,v,l,M);
if(x>M)modify(RC,x,v,M+1,r);
up(p);
}
PII quary(int p,int x,int y,int l,int r){
if(x>y)return make_pair(0,0);
if(x<=l&&r<=y)return ss[p];
PII res=make_pair(0,0);
if(x<=M){
PII tmp=quary(LC,x,y,l,M);
res.first=(res.first+tmp.first)%mod;
res.second=(res.second+tmp.second)%mod;
}
if(y>M){
PII tmp=quary(RC,x,y,M+1,r);
res.first=(res.first+tmp.first)%mod;
res.second=(res.second+tmp.second)%mod;
}
return res;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
getchar();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
char tmp;
scanf("%c",&tmp);
if(tmp=='1'){
modify(1,i,1,1,n);
ans=(ans+i*(cnt++)-sumn)%mod;
sumn+=i;
}
}
scanf("%d",&m);
printf("%lld\n",ans);
while(m--){
int op,pos;
scanf("%d%d",&op,&pos);
if(op==1){
modify(1,pos,1,1,n);
PII l=quary(1,1,pos-1,1,n),r=quary(1,pos+1,n,1,n);
long long LA=(l.second*pos-l.first+mod)%mod,RA=(r.first-r.second*pos+mod)%mod;
ans=(ans+LA+RA+mod)%mod;
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
else{
modify(1,pos,-1,1,n);
PII l=quary(1,1,pos-1,1,n),r=quary(1,pos+1,n,1,n);
long long LA=(l.second*pos-l.first+mod)%mod,RA=(r.first-r.second*pos+mod)%mod;
ans=(ans-LA-RA+mod*2)%mod;
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
}
}H:牛牛的k合因子数
 输入
输入
10 5
1
2
3
4
5输出
4
1
0
0
0说明
1~10的范围内
1合因子数有:4,6,9,10,共4个
2合因子数有:8,共1一个使用埃筛即可出解
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool is_prime[100050];
int n,m,num_hy[100050];
void es(){
memset(is_prime,true,sizeof(is_prime));
is_prime[0]=is_prime[1]=false;
for(int i = 2; i*i <= n; i ++){//判断改成i*i<N
if(is_prime[i]){
for(int j = i*i; j <= n; j += i){//从i*i开始就可以了
is_prime[j] = false;
}
}
}
is_prime[0]=is_prime[1]=true;
}
void jduge(){
for(int i=1;i*i<=n;i++){
for(int j=i;i*j<=n;j++){
if(!is_prime[i]){num_hy[i*j]++;}//cout<<">>> "<<i*j<<" have a hyz "<<i<<endl;}
if(!is_prime[j]){num_hy[i*j]++;}//cout<<">>> "<<i*j<<" have a hyz "<<j<<endl;}
if(i==j&&!is_prime[j]){num_hy[i*j]--;}//cout<<">>> "<<i*j<<" -- "<<j<<endl;}
}
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
es();
jduge();
sort(num_hy+1,num_hy+n+1);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
int k;
scanf("%d",&k);
printf("%d\n",upper_bound(num_hy+1,num_hy+1+n,k)-lower_bound(num_hy+1,num_hy+1+n,k));
}
// cout<<"-------------------------------------------------"<<endl;
// for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cout<<num_hy[i]<<" ";
return 0;
}I:牛牛的汉诺塔

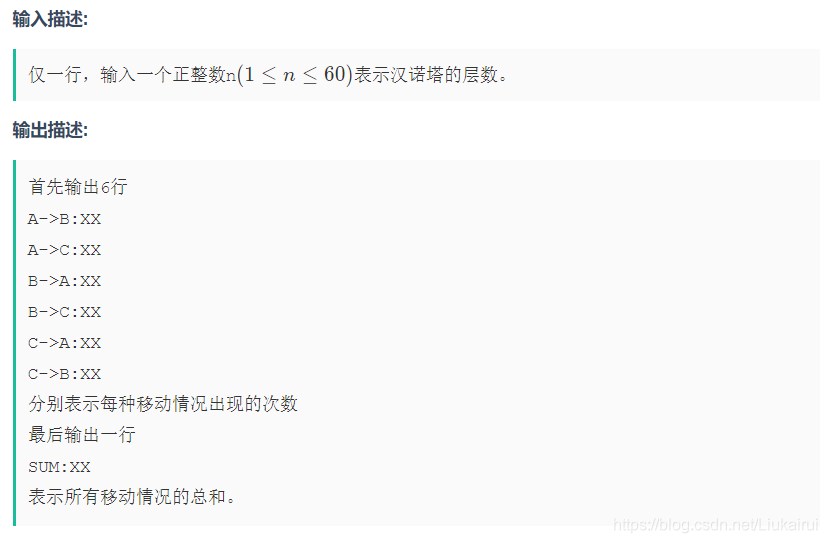 输入
输入
3输出
A->B:1
A->C:3
B->A:1
B->C:1
C->A:0
C->B:1
SUM:7说明
A->C
A->B
C->B
A->C
B->A
B->C
A->C
统计:
A->B出现1次
A->C出现3次
B->C出现1次
B->A出现1次
C->B出现1次
总计7次首先要解决的是总数的问题\(2^{n-1}\) 解法见此
写下n=2-5的所有过程,可以发现规律
A->B=(上一次)A->C->B
B->C=(上一次)B->A->C
C->A=(上一次)C->B->A#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
long long ans[70][10]={
{0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 } ,
{1 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 3 } ,
{1 , 3 , 1 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 7 } ,
{4 , 3 , 1 , 4 , 2 , 1 , 15 } ,
{4 , 9 , 6 , 4 , 2 , 6 , 31 } ,
{15 , 9 , 6 , 15 , 12 , 6 , 63 } ,
{15 , 31 , 27 , 15 , 12 , 27 , 127 } ,
{58 , 31 , 27 , 58 , 54 , 27 , 255 } ,
{58 , 117 , 112 , 58 , 54 , 112 , 511 } ,
{229 , 117 , 112 , 229 , 224 , 112 , 1023 } ,
{229 , 459 , 453 , 229 , 224 , 453 , 2047 } ,
{912 , 459 , 453 , 912 , 906 , 453 , 4095 } ,
{912 , 1825 , 1818 , 912 , 906 , 1818 , 8191 } ,
{3643 , 1825 , 1818 , 3643 , 3636 , 1818 , 16383 } ,
{3643 , 7287 , 7279 , 3643 , 3636 , 7279 , 32767 } ,
{14566 , 7287 , 7279 , 14566 , 14558 , 7279 , 65535 } ,
{14566 , 29133 , 29124 , 14566 , 14558 , 29124 , 131071 } ,
{58257 , 29133 , 29124 , 58257 , 58248 , 29124 , 262143 } ,
{58257 , 116515 , 116505 , 58257 , 58248 , 116505 , 524287 } ,
{233020 , 116515 , 116505 , 233020 , 233010 , 116505 , 1048575 } ,
{233020 , 466041 , 466030 , 233020 , 233010 , 466030 , 2097151 } ,
{932071 , 466041 , 466030 , 932071 , 932060 , 466030 , 4194303 } ,
{932071 , 1864143 , 1864131 , 932071 , 932060 , 1864131 , 8388607 } ,
{3728274 , 1864143 , 1864131 , 3728274 , 3728262 , 1864131 , 16777215 } ,
{3728274 , 7456549 , 7456536 , 3728274 , 3728262 , 7456536 , 33554431 } ,
{14913085 , 7456549 , 7456536 , 14913085 , 14913072 , 7456536 , 67108863 } ,
{14913085 , 29826171 , 29826157 , 14913085 , 14913072 , 29826157 , 134217727 } ,
{59652328 , 29826171 , 29826157 , 59652328 , 59652314 , 29826157 , 268435455 } ,
{59652328 , 119304657 , 119304642 , 59652328 , 59652314 , 119304642 , 536870911 } ,
{238609299 , 119304657 , 119304642 , 238609299 , 238609284 , 119304642 , 1073741823 } ,
{238609299 , 477218599 , 477218583 , 238609299 , 238609284 , 477218583 , 2147483647 } ,
{954437182 , 477218599 , 477218583 , 954437182 , 954437166 , 477218583 , 4294967295 } ,
{954437182 , 1908874365 , 1908874348 , 954437182 , 954437166 , 1908874348 , 8589934591 } ,
{3817748713 , 1908874365 , 1908874348 , 3817748713 , 3817748696 , 1908874348 , 17179869183 } ,
{3817748713 , 7635497427 , 7635497409 , 3817748713 , 3817748696 , 7635497409 , 34359738367 } ,
{15270994836 , 7635497427 , 7635497409 , 15270994836 , 15270994818 , 7635497409 , 68719476735 } ,
{15270994836 , 30541989673 , 30541989654 , 15270994836 , 15270994818 , 30541989654 , 137438953471 } ,
{61083979327 , 30541989673 , 30541989654 , 61083979327 , 61083979308 , 30541989654 , 274877906943 } ,
{61083979327 , 122167958655 , 122167958635 , 61083979327 , 61083979308 , 122167958635 , 549755813887 } ,
{244335917290 , 122167958655 , 122167958635 , 244335917290 , 244335917270 , 122167958635 , 1099511627775 } ,
{244335917290 , 488671834581 , 488671834560 , 244335917290 , 244335917270 , 488671834560 , 2199023255551 } ,
{977343669141 , 488671834581 , 488671834560 , 977343669141 , 977343669120 , 488671834560 , 4398046511103 } ,
{977343669141 , 1954687338283 , 1954687338261 , 977343669141 , 977343669120 , 1954687338261 , 8796093022207 } ,
{3909374676544 , 1954687338283 , 1954687338261 , 3909374676544 , 3909374676522 , 1954687338261 , 17592186044415 } ,
{3909374676544 , 7818749353089 , 7818749353066 , 3909374676544 , 3909374676522 , 7818749353066 , 35184372088831 } ,
{15637498706155 , 7818749353089 , 7818749353066 , 15637498706155 , 15637498706132 , 7818749353066 , 70368744177663 } ,
{15637498706155 , 31274997412311 , 31274997412287 , 15637498706155 , 15637498706132 , 31274997412287 , 140737488355327 } ,
{62549994824598 , 31274997412311 , 31274997412287 , 62549994824598 , 62549994824574 , 31274997412287 , 281474976710655 } ,
{62549994824598 , 125099989649197 , 125099989649172 , 62549994824598 , 62549994824574 , 125099989649172 , 562949953421311 } ,
{250199979298369 , 125099989649197 , 125099989649172 , 250199979298369 , 250199979298344 , 125099989649172 , 1125899906842623 } ,
{250199979298369 , 500399958596739 , 500399958596713 , 250199979298369 , 250199979298344 , 500399958596713 , 2251799813685247 } ,
{1000799917193452 , 500399958596739 , 500399958596713 , 1000799917193452 , 1000799917193426 , 500399958596713 , 4503599627370495 } ,
{1000799917193452 , 2001599834386905 , 2001599834386878 , 1000799917193452 , 1000799917193426 , 2001599834386878 , 9007199254740991 } ,
{4003199668773783 , 2001599834386905 , 2001599834386878 , 4003199668773783 , 4003199668773756 , 2001599834386878 , 18014398509481983 } ,
{4003199668773783 , 8006399337547567 , 8006399337547539 , 4003199668773783 , 4003199668773756 , 8006399337547539 , 36028797018963967 } ,
{16012798675095106 , 8006399337547567 , 8006399337547539 , 16012798675095106 , 16012798675095078 , 8006399337547539 , 72057594037927935 } ,
{16012798675095106 , 32025597350190213 , 32025597350190184 , 16012798675095106 , 16012798675095078 , 32025597350190184 , 144115188075855871 } ,
{64051194700380397 , 32025597350190213 , 32025597350190184 , 64051194700380397 , 64051194700380368 , 32025597350190184 , 288230376151711743 } ,
{64051194700380397 , 128102389400760795 , 128102389400760765 , 64051194700380397 , 64051194700380368 , 128102389400760765 , 576460752303423487 } ,
{256204778801521560 , 128102389400760795 , 128102389400760765 , 256204778801521560 , 256204778801521530 , 128102389400760765 , 1152921504606846975 }
};
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
cout<<"A->B:"<<ans[n-1][0]<<endl;
cout<<"A->C:"<<ans[n-1][1]<<endl;
cout<<"B->A:"<<ans[n-1][2]<<endl;
cout<<"B->C:"<<ans[n-1][3]<<endl;
cout<<"C->A:"<<ans[n-1][4]<<endl;
cout<<"C->B:"<<ans[n-1][5]<<endl;
cout<<"SUM:"<<ans[n-1][6];
}J: 牛牛的宝可梦Go
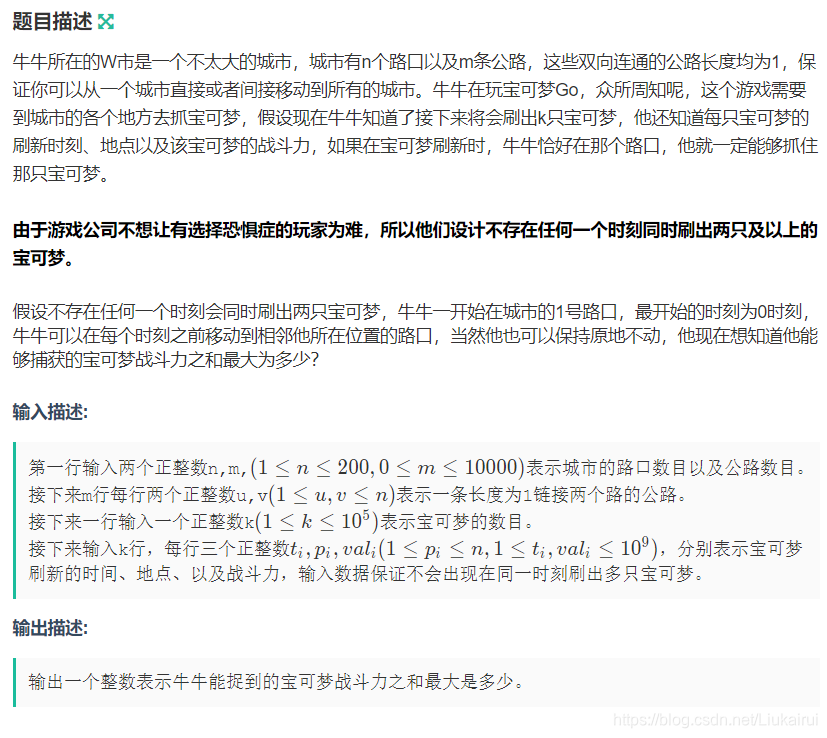 输入
输入
3 2
1 2
2 3
3
1 1 5
2 3 10
3 2 1输出
11输入
1 0
3
1 1 100
100 1 10000
10000 1 1输出
10101输入
3 2
1 2
2 3
1
1 3 1000000000输出
0输入
3 2
1 2
2 3
1
1 2 1000000000输出
1000000000这个题首先先求一遍最短路,这个求最短路的过程可以用flord实现。 接下来类似最长上升子序列,但是显然这个好像不太好优化,考虑暴力\(k^2\)转移,由于地图的大小只有200,所以200步以后可以转移到任意位置,用这个性质可以优化\(k^2\)->200k。 也就是说每次转移只暴力往前for200个,多余200个以上的时候记录一个前缀max,直接从这个前缀中转移。 时间复杂度:\(O\left(200k\right)\)
#include<cstdio>
#include<cctype>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define il inline
#define ll long long
il char gc() {
static char buf[1<<24],*p1=buf,*p2=buf;
return p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,1<<24,stdin),p1==p2)? EOF:*p1++;
}
#define gc getchar
il int inn() {
int x=0,c=gc();
bool f=0;
for(; !isdigit(c); c=gc()) if(c=='-') f=1;
if(f) for(; isdigit(c); c=gc()) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)-(c^48);
else for(; isdigit(c); c=gc()) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48);
return x;
}
const int N=205;
const int K=100005;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,m,k,l,mp[N][N];
struct node {
int t,p,v;
}a[K];
ll f[K],ans,mx;
void floyd() {
for(int k=1; k<=n; ++k) {
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) {
for(int j=1; j<=n; ++j) {
mp[i][j]=min(mp[i][j],mp[i][k]+mp[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
bool cmp(const node &a,const node &b) {
return a.t<b.t;
}
int main() {
n=inn(),m=inn();
memset(mp,0x3f,sizeof(mp));
for(int i=1; i<=m; ++i) {
int u=inn(),v=inn();
mp[u][v]=mp[v][u]=1;
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) mp[i][i]=0;
floyd();
k=inn();
for(int i=1; i<=k; ++i) {
a[i].t=inn(),a[i].p=inn(),a[i].v=inn();
if(mp[1][a[i].p]==inf) { --i,--k,--n; }
}
sort(a+1,a+k+1,cmp);
a[0].p=1;
for(int i=1; i<=k; ++i) {
if(mp[1][a[i].p]>a[i].t) continue;
while(a[i].t-a[l].t>=n) {
mx=max(mx,f[l++]);
}
f[i]=mx;
for(int j=l; j<i; ++j) {
if(mp[a[j].p][a[i].p]<=a[i].t-a[j].t) {
f[i]=max(f[i],f[j]);
}
}
f[i]+=a[i].v;
ans=max(ans,f[i]);
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
return 0;
}